 African Medical Devices Forum
African Medical Devices Forum
On-line learning exercise
In the document below we present some examples of the type of issues that may be encountered when assessing evidence submitted by manufacturers on the clinical performance of their product.
Please complete the following tasks:
1. Conduct an assessment of the clinical performance study summaries.
2. Generate questions to the manufacturer in the following format
a) What did the manufacturer say or do? b) What is the issue? c) What information do you need or how can the issue be corrected?
3. When you have finished reviewing the document compare your comments with those on the review page by clicking here
1. DEVICE NAME
The VL HIV Test
2. INDICATIONS FOR USE
The VL HIV is a rapid in vitro nucleic acid amplification test for the quantitation of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) nucleic acid in human plasma and fingerstick whole blood, using the VL Instrument Analyzer for sample preparation and the VL Analyzer for automated amplification and detection. This test is intended for use at the point of care in conjunction with clinical presentation and other laboratory markers of disease progress for the clinical management of HIV-infected patients.
3. DEVICE DESCRIPTION
The device consists of two components, the VL HIV Test cartridge (single use with all necessary reagents that work within a microfluidics system) and the VL Instrument Analyzer. After introduction of the specimen to the VL HIV Test cartridge, the cartridge is loaded onto the VL Instrument Analyzer. Three processes then take place:
4. SUMMARY OF CLINICAL PERFORMANCE
Clinical Sensitivity and Specificity
Methodology
This study was designed to evaluate the clinical specificity and sensitivity of the VL HIV Test by testing fresh and frozen samples collected from normal healthy donors and patients with HIV-1. This study compared test results obtained with the VL HIV Test to those obtained with either the Roche COBAS AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR Test, v1.5 (CA), the Roche COBAS AmpliScreen HIV-1 Test, ver 1.5 (blood donor screening test), or a research use HIV PCR assay. Clinical specificity of the VL HIV Test was evaluated by testing 399 frozen samples and 120 fresh samples, in EDTA plasma, collected from normal healthy blood donors who were negative for HIV-1 antibodies. Frozen samples were randomly distributed across testing sites. Fresh samples were distributed to testing sites in a non-random manner. Clinical sensitivity of the VL HIV TEST was evaluated testing 351 frozen samples with HIV-1 RNA concentrations ≥50 cp/mL and 122 fresh samples in EDTA plasma, collected from HIV-1-positive blood donors. Frozen samples were randomly distributed across testing sites, stratified by CD4 count category. Fresh samples were distributed to testing sites in a non-random manner. Collection of frozen normal donor (HIV-1-negative) samples occurred at 2 sites in Arusha Collection of frozen HIV-1-positive samples occurred at 1 site (Nairobi). Collection of fresh samples occurred at 3 sites [London (UK), Washington, DC, (USA) and Cape Town (SA)]; samples from normal healthy donors were collected at 1 site in Geneva, Switzerland. Fresh samples collected for this study were tested prospectively on the VL platform. Testing was performed at The VL Company’s laboratories using 1 VL Analyzer system per site, with 1 reagent/cartridge lot.
Statistical Methods
Normal subjects were considered evaluable if they contributed both valid VL HIV Test and comparator test results (where the comparator result was Target Not Detected). HIV-1 subjects were considered evaluable if they contributed both valid VL HIV Test and comparator results (where the comparator result was ≥50 copies/mL).
VL HIV Test clinical specificity was calculated as the percentage of normal subjects with Target Not Detected comparator test results, who had Target Not Detected VL HIV Test results. VL HIV Test clinical specificity was calculated overall and by sample type (fresh and frozen separately).
VL HIV Test clinical sensitivity was calculated as the percentage of HIV-1 subjects with comparator test results ≥50 cp/mL, who had detectable HIV-1 viral load on the VL HIV Test. VL HIV Test clinical sensitivity was calculated overall and by CD4 count category (<200, >500 cells/uL) and sample type (fresh and frozen separately).
Table 1 summarizes the number of fresh and frozen samples from evaluable normal and HIV-1 subjects in this study.
- Specimen preparation to isolate HIV RNA
- Reverse transcription of RNA and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) amplification of the resultant cDNA
- Detection of amplified cDNA (amplicon)
TABLE 1: Number of Evaluable Normal and HIV-1 Subjects by Sample Type
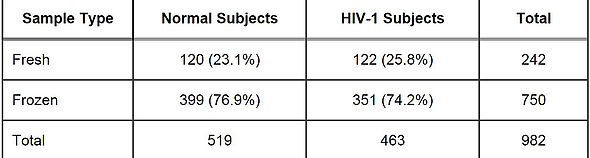
Table 2 shows the VLHIV Test clinical specificity results from the 519 evaluable normal subjects. The VLHIV Test clinical specificity was 100% (519/519)
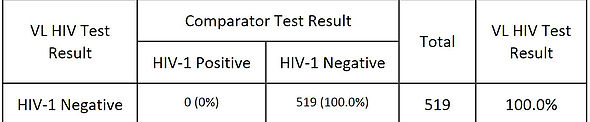
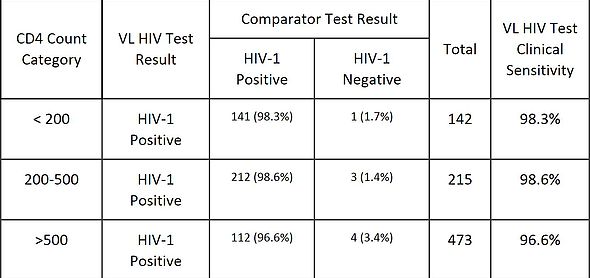
Table 3 shows the VLHIC Test clinical senstivity results from the 473 evaluable HIV-1 subjects. The VL HIV Test clinical sensitivity was 98.3%.
TABLE 3: VL HIV Test Sensitivity - Evaluable Normal Subjects

All 8 samples that were determined to be positive for HIV-1 by the VL HIV test but not by the comparator test had a low copy number: 6 of the 8 had HIV-1 titers of <100cp/mL, 1 had a titre of 253 cp/mL, and the remaining sample had a titer of 479 cp/mL.
Table 4 shows the VL HIV Test clinical senstivity by CD4 count category (,200, 200-500, >500 cells/μL).
TABLE 4: VL HIV Test Sensitivity - Evaluable Normal Subjects
Conclusion
When compared with results from the comparator tests, clinical specificity of the VL HIV Test was 100% and clinical sensitivity was 98.3%.
The VL HIV Test also showed similar clinical sensitivity among CD4 count categories (>96% overall), suggesting comparable performance in samples from HIV-1 patients with various CD4 counts.

©2024 African Medical Devices Forum (AMDF)
Improving Access to Affordable Diagnostics